Authentication Mechanisms
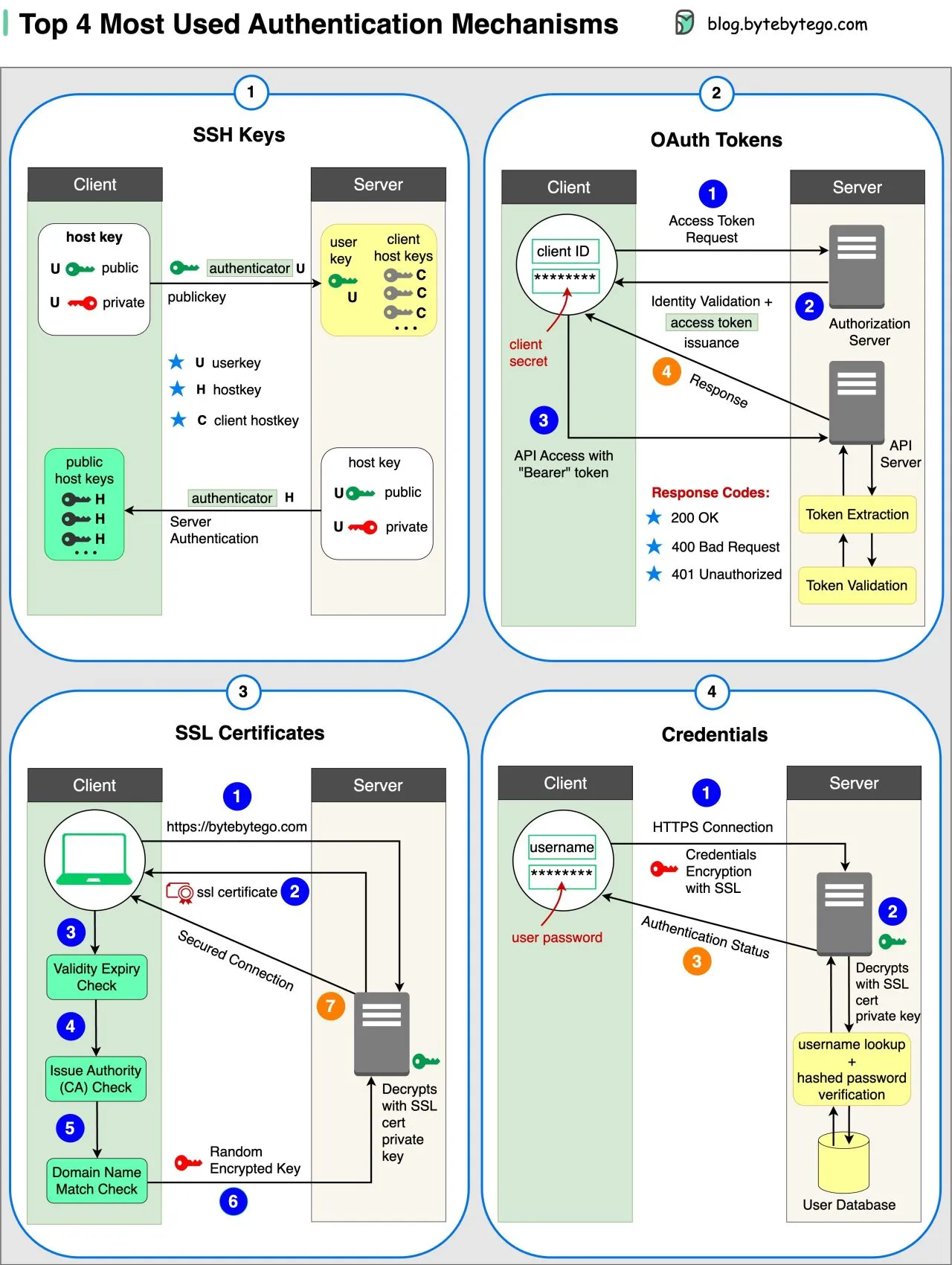
SSH Keys
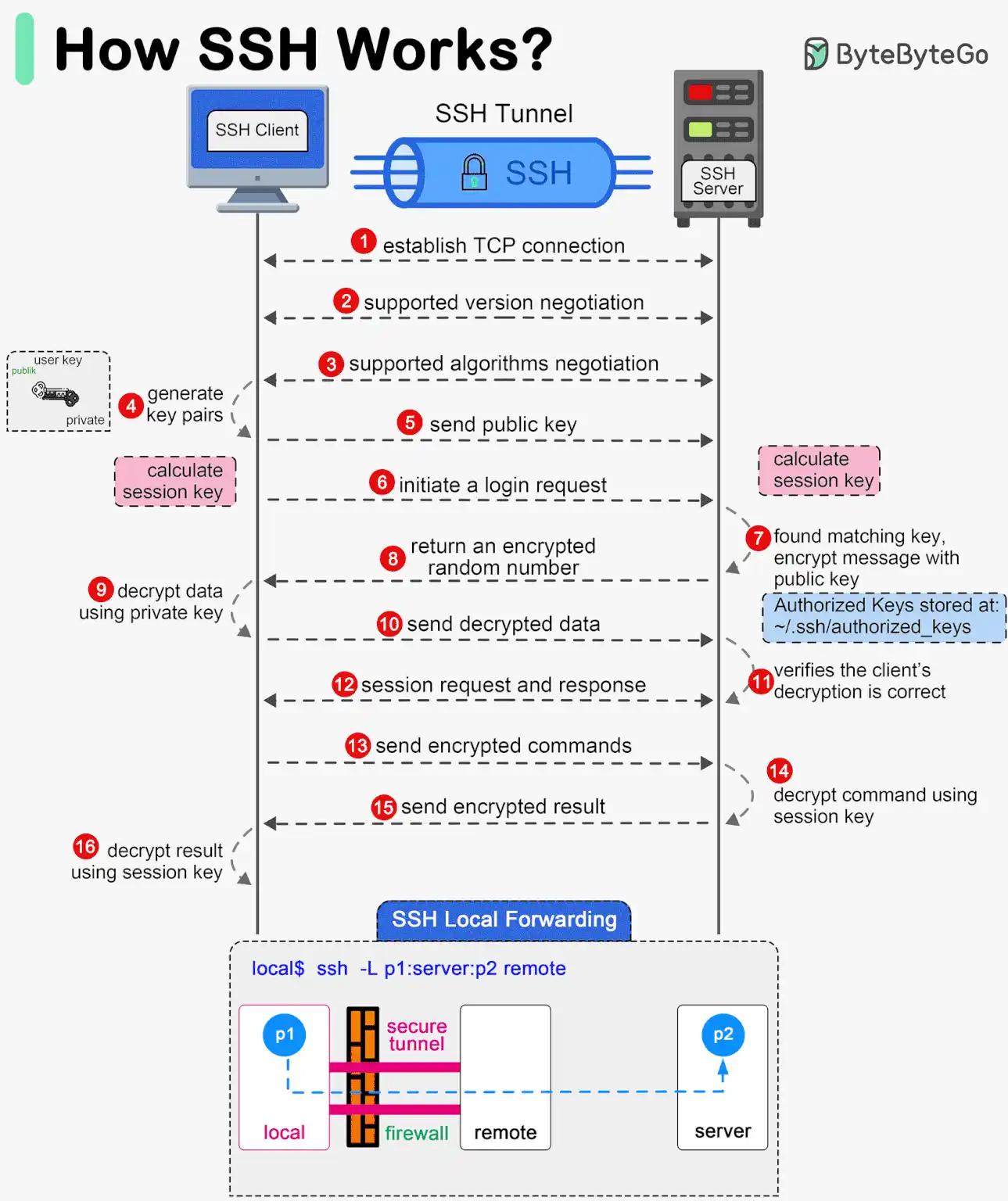
SSH (Secure Shell) is a network protocol used to securely connect to remote machines over an unsecured network. It encrypts the connection and provides various mechanisms for authentication and data transfer.
OAuth Tokens
Tokens that provide limited access to user data on third-party applications
SSL Certificates
Digital certificates ensure secure and encrypted communication between servers and clients
Credentials
User authentication information is used to verify and grant access to various systems and services
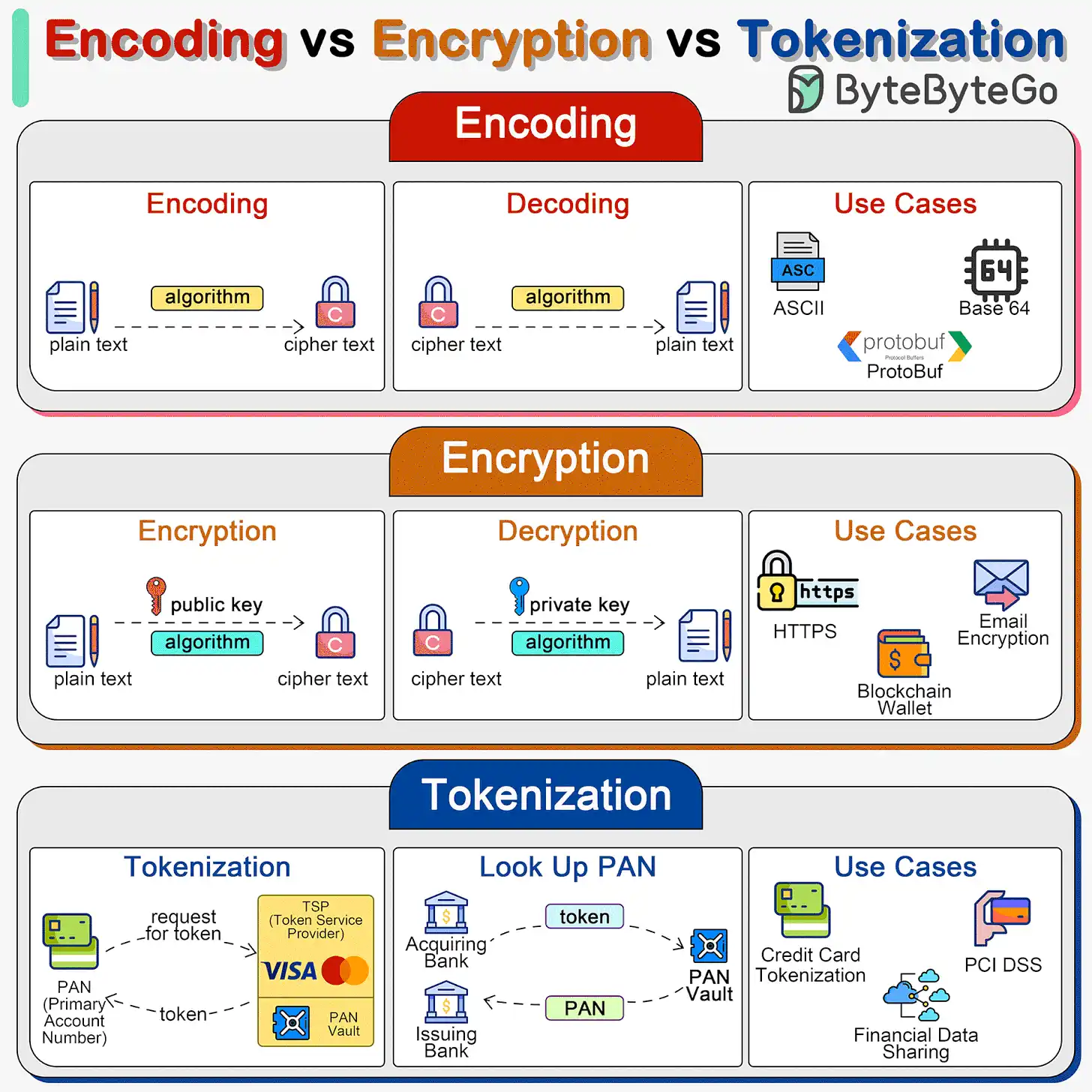
Encoding vs Encryption vs Tokenization
ByteByteGo.com
-
Encoding
Encoding converts data into a different format using a scheme that can be easily reversed. Examples include Base64 encoding, which encodes binary data into ASCII characters, making it easier to transmit data over media that are designed to deal with textual data.
Encoding is not meant for securing data. The encoded data can be easily decoded using the same scheme without the need for a key.
-
Encryption
Encryption involves complex algorithms that use keys for transforming data. Encryption can be symmetric (using the same key for encryption and decryption) or asymmetric (using a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption).
Encryption is designed to protect data confidentiality by transforming readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using an algorithm and a secret key. Only those with the correct key can decrypt and access the original data.
-
Tokenization
Tokenization is the process of substituting sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholders called tokens. The mapping between the original data and the token is stored securely in a token vault. These tokens can be used in various systems and processes without exposing the original data, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Tokenization is often used for protecting credit card information, personal identification numbers, and other sensitive data. Tokenization is highly secure, as the tokens do not contain any part of the original data and thus cannot be reverse-engineered to reveal the original data. It is particularly useful for compliance with regulations like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).